CMES makes the robot 'eyes'...'A perfect fix' to automation
Recognize objects in 3 dimensions
Perform processes with many variables
Increase demand in various fields such as logistics
Suitable for small batch production of multi-type of products
Manufacturing plants have always pursued factory automation. However, some processes are still done by a human. This is the case when it is a task that creates variables. Picking up randomly pouring boxes is easy for humans, but complex tasks for robots. This is because there is no 'eye' that perceives objects in three dimensions and the 'brain' that analyzes them and connects them with actions.
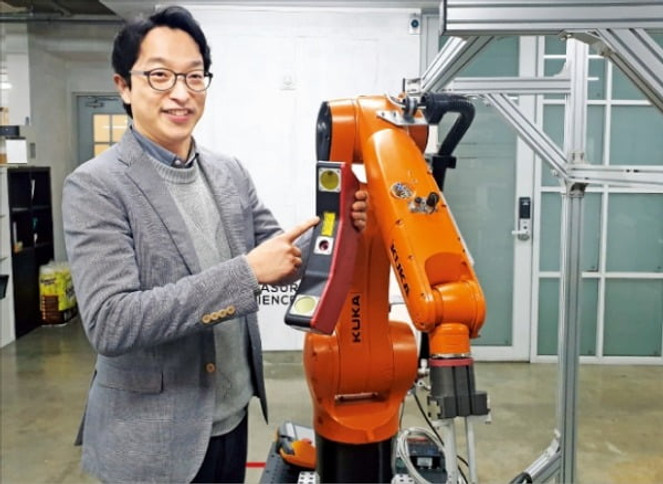
CMES is a company that gives robots 'eyes' and a 'brain'. When a 3D vision sensor is installed and linked with an existing robot with software, it recognizes and responds to an object.
In factories of large corporations such as Hyundai Motor Company and LG Electronics, CMES robots with 'eyes' are active.
Sungho Lee, CEO of CMES said, "If you use a 3D vision sensor, you can use robots even in processes where automation was difficult."
Development of 'eyes' of robots
CMES is a robot control technology company founded in 2014 by Lee, a former researcher. CEO Lee founded a company with colleagues while working for Orbotech, an Israeli liquid crystal display (LCD) inspection equipment company. Initially, it mainly supplied inspection equipment that recognizes small objects in three dimensions. It is a device that inspects defects by identifying small objects up to 5 to 10 μm (1 μm = 1 millionth of a meter) in three dimensions. A 3D scanner that recognizes microscopic objects is a key technology.
CMES is a robot control technology company founded in 2014 by Lee, a former researcher. CEO Lee founded a company with colleagues while working for Orbotech, an Israeli liquid crystal display (LCD) inspection equipment company. Initially, it mainly supplied inspection equipment that recognizes small objects in three dimensions. It is a device that inspects defects by identifying small objects up to 5 to 10 μm (1 μm = 1 millionth of a meter) in three dimensions. A 3D scanner that recognizes microscopic objects is a key technology.
Mando, an automobile parts company, is a representative example. Mando has automated placing auto parts on pallets (cargo transport brackets) using CMES robot control technology. Previously, the shape of each pallet was different, which was what people were doing. Worker injuries were also frequent because parts over 10 kg had to be lifted and placed all day long. CEO Lee explained, “This is an example of replacing the work that three people had been doing in three shifts with a robot.”
Compatible with small quantity production of multi-type of products
According to the company, CMES robot control technology is suitable for small-scale production of various types. It is different from existing factory automation technology suitable for mass production of small items. Representative Lee cited the example of a customer company that produces a global shoe brand.
In the existing production process, when bonding was applied to the soles of shoes, the same side's soles and the same size were collected and produced at once. This is because the robot could only repeat the same movement. Using CMES robot control technology gives crucial benefits. There is no problem even if the left and right, large and small sizes that appear irregularly. Recognize the shape of individual soles and apply bond.
From the beginning, it has secured large corporate clients and made steady results while making plans to be listed on the stock market. It plans to list Samsung Securities last year as the subject of listing and list it next year or later. CEO Lee said, “The demand for atypical factory automation will expand beyond labor-intensive consumer goods such as shoes and automobiles to various fields such as logistics.” I will do it.”
Source: The Korea Economic Daily, 5 Feb. 2020
https://www.hankyung.com/economy/article/202002036209i